CYBER SECURITY
What is Cyber Security?
The technique of protecting internet-connected systems such as computers, servers, mobile devices, electronic systems, networks, and data from malicious attacks is known as cybersecurity. We can divide cybersecurity into two parts one is cyber, and the other is security. Cyber refers to the technology that includes systems, networks, programs, and data. And security is concerned with the protection of systems, networks, applications, and information. In some cases, it is also called electronic information security or information technology security.
Some other definitions of cybersecurity
are:
 |
| DATA BREACH |
"Cyber Security is the body of technologies, processes, and practices designed to protect networks, devices, programs, and data from attack, theft, damage, modification or unauthorized access."
"Cyber Security is the set of principles and practices designed to protect our computing resources and online information against threats."
Why Is Cybersecurity Important?
One of the many advantages to living in a world where every device is connected is convenience. It’s incredibly easy to conduct work, manage your social calendar, shop and make appointments from your smartphone or device. That’s why it’s become second nature to many of us.
But, of course, the convenience of connected data also means threats from bad actors can do a lot of damage. Cybersecurity initiatives are essential to protecting our data and thus, our way of life.
BIGGEST CYBER ATTACKS IN HISTORY
Estonia
jammed cyber attack in 2007
In April and May 2007, hackers unleashed a wave of cyber attacks that crippled dozens of government and corporate sites in Estonia, one of Europe's most wired countries. Estonian authorities traced the so-called denial of service attacks to Russia, and suggested they had been orchestrated by the Kremlin — a charge Moscow denied.
The online assault followed Estonia's decision to move a Soviet World War II memorial from downtown Tallinn on April 27, 2007, sparking furious protests from Russia's government and rioting among Estonia's ethnic Russian minority.
Experts said hundreds of thousands of computers were used in a coordinated attack against government agencies and banks.
Cyberattack on Critical Infrastructure: Russia and the Ukrainian
Power Grid Attacks
Regional electricity
distribution company Ukrainian Kyivoblenergo has a dubious distinction. It is
the world’s first power grid provider to be taken down in a cyber attack.
It all began when its Prykarpattyaoblenergo control center was the victim of a cyber intrusion on December 23, 2015. The company’s computer and SCADA systems were attacked, disconnecting 30 substations for three hours. As many as 230,000 customers lost power – approximately half of the homes in the Ivano-Frankivsk region in Ukraine (population about 1.4 million). The tool used was malware known as BlackEnergy
Ukrainian
government officials came out rather quickly to claim the outages were caused
by a cyber attack, squarely placing blame on Russian security services.
(1991) 21
DAY STUT DOWN CYBER CRIME NANA computer
The 1999
Nana Cyber Attacks, also known as the "Nana" virus or the
"Bubble Boy" virus, were a series of coordinated cyberattacks that
targeted Microsoft Windows systems around the world. The virus was named after
the name "Nana" that appeared in the code.
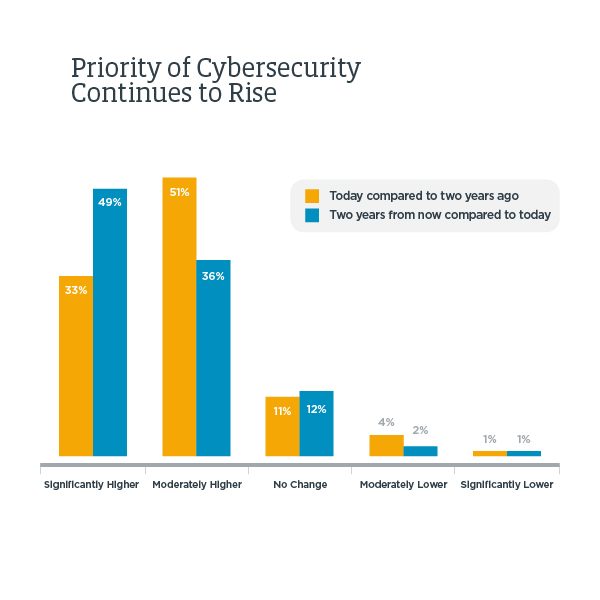
It’s time for the
statistics derived from the Cyber Attacks Timelines of November (Part I and Part II).
Let us begin with
the Country Distribution chart that, easy
predictable, shows the US on top of all categories. However, globally, even
Italy, Canada and UK show up, respectively for Hacktivism (the first two
countries) and Cyber Crime (the latter).
The Daily
Trend of Attacks chart shows a moderate activity with a peak on the
10th, and a plateau between the 13th and 14th. Despite the 5th of November is a
day felt by Hacktivists, no noticeable operations have been recorded this year.
Once again Cyber Crime leads the Motivations Behind Attacks chart with 55.8%
substantially in line with the previous month (was around 60%). Hacktivism
ranks at number two with 28.6%, a remarkable increase compared to 13.8% of
October. Whereas Cyber Espionage remains quite high (13%, despite in decrease
compared to the record value of 17.2% recorded in October.
Cyber crime stories of 2012
Cyber crime has continued to become more professional in 2012, with the barriers to entry becoming ever lower with the emergence of increasingly powerful toolkits and exploits for sale o the past year, cyber criminals have used increasingly powerful and targeted attacks to steal information ranging from credit card details and other personal information to intellectual property
1999
CYBER CRIME Macro Viruses
Macro viruses involving infected Word and Excel files were a plague in
the late 1990s. Yet, like grunge music, the genre fell into decline as
techniques and technologies moved on. More recently macro viruses have staged
something of a revival, thanks to social-engineering trickery.
Windows executable malware has dominated macro
viruses written in VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) since the turn of the century.
Users opening an infected document were exposed to
malicious code that infected Windows PCs. The macro virus would spread into a
user's Office template files before sneaking copies of itself into any
subsequently edited documents. Examples of macro-based malware include the
fast-spreading Melissa email worm from 1999.
Security improvements in Microsoft Office products
blocked many such attacks, propelling macro viruses towards extinction in the
process
TOP 10 BIGGEST CYBER ATTACKS IN HISTORY
VIDEO LINK :
Types of Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity can be categorized into five distinct types:**8ZZz
1 Critical infrastructure security
2 Application security
3 Network security
4 Cloud security
5 Internet of Things (IoT) security
To cover all of its bases, an organization should develop a comprehensive plan that includes not only these five types of cybersecurity, but also the three components that play active roles in a cybersecurity posture: people, processes and technology.
Critical infrastructure security
Critical infrastructure security is the area of concern surrounding the protection of systems, networks and assets whose continuous operation is deemed necessary to ensure the security of a given nation, its economy, and the public’s health and/or safety.
Application
security
Application
security is the process of developing, adding, and testing security features
within applications to prevent security vulnerabilities against threats such as
unauthorized access and modification.
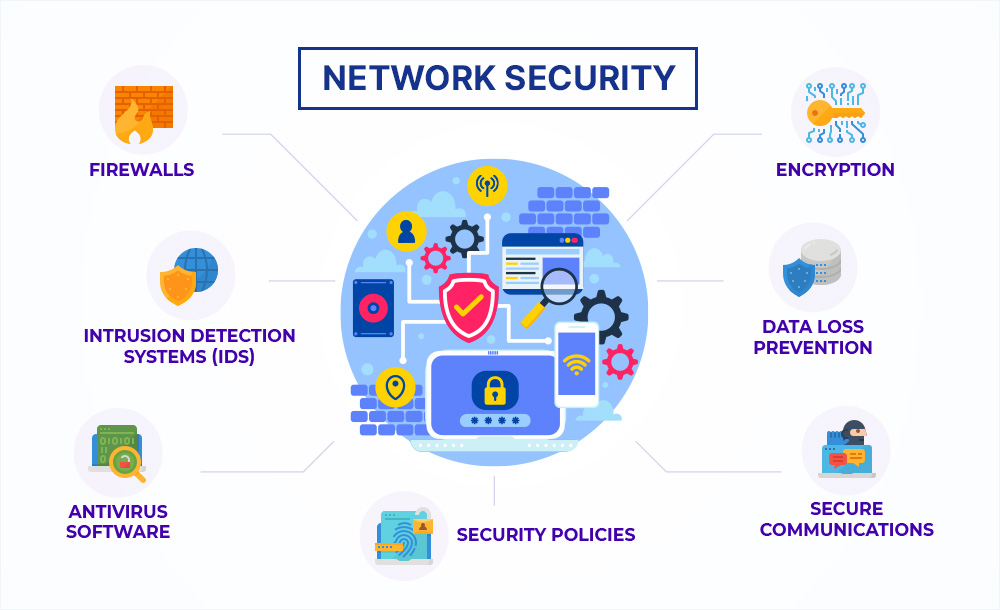
Network
security
Network security is a set of technologies that protects the usability and integrity of a company's infrastructure by preventing the entry or proliferation within a network of a wide variety of potential threats.
Cloud
security
Cloud
security, also known as cloud computing security, is a collection of security
measures designed to protect cloud-based infrastructure, applications, and
data. These measures ensure user and device authentication, data and resource
access control, and data privacy protection. They also support regulatory data
compliance. Cloud security is employed in cloud environments to protect a
company's data from distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks, malware,
hackers, and unauthorized user access or use.
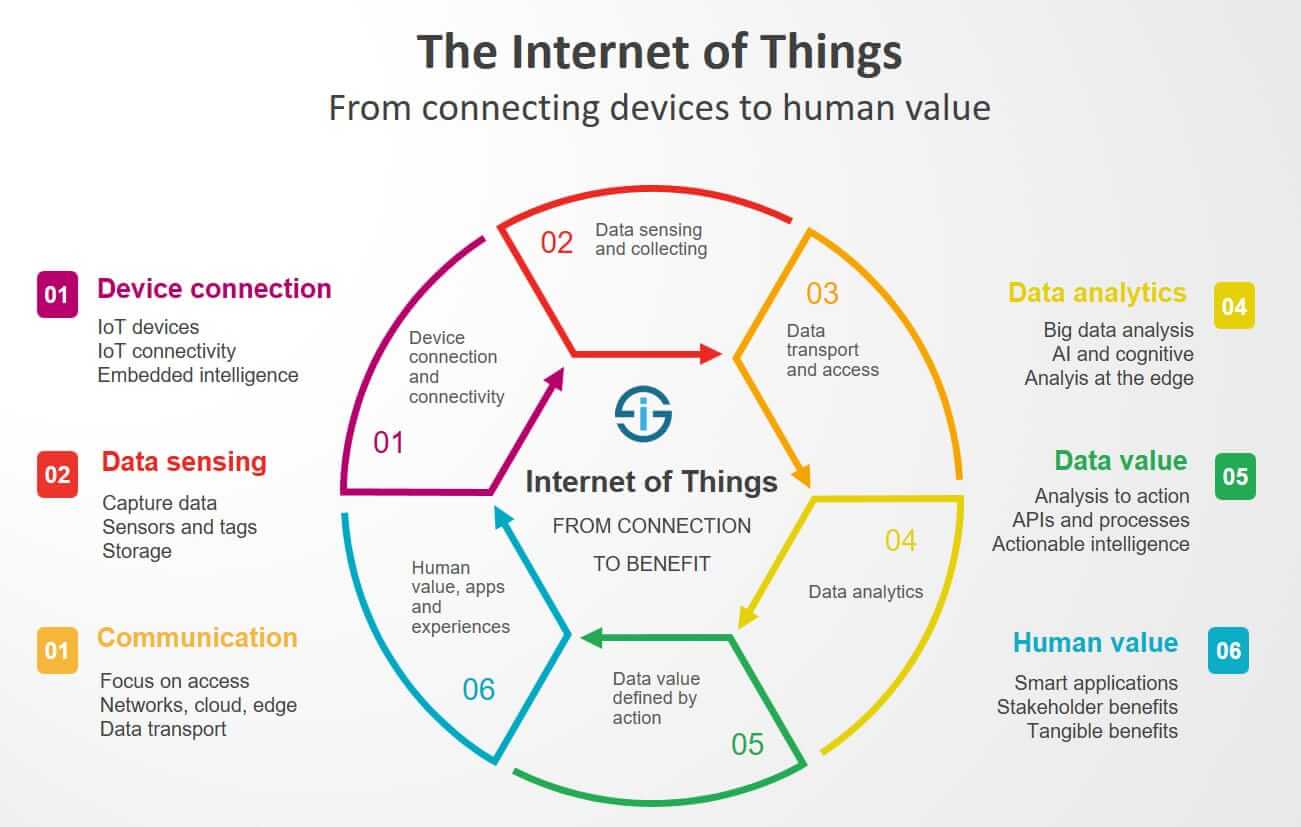
Internet of
things (iot) security
IOT Security
is the act of securing Internet devices and the networks they're connected to
from threats and breaches by protecting, identifying, and monitoring risks all
while helping fix vulnerabilities from a range of devices that can pose
security risks to your business.
Effects of CyberCrime
According to a
2018 report published by McAfee, the economic impact of cybercrimes
is estimated to cost the global economy nearly $600 billion annually.
Financial loss is
one of the obvious effects of cybercrimes, and it can be quite significant. But
cyber crimes also have several other disastrous consequences for businesses
such as:
1.Investor perception can become a huge problem after a security breach
causing a drop in the value of businesses.
2. Businesses may also face increased costs for borrowing, and raising
more capital can be challenging as well after a security breach.
3.Loss of sensitive customer data can result in penalties and fines for
failing to protect customer data. Businesses may be sued over data breaches.
4.Due to loss of reputation and damaged brand identity after a
cyberattack, customers’ trust in a business will decline. Businesses not only
end up losing current customers but also find it difficult to gain new
customers.
5. Direct costs may also be incurred such as the cost of hiring cybersecurity companies for remediation, increased insurance premium costs, public relations (PR), and other services related to the attack.
Cyber Security and CyberCrime
Cyber security is a
domain that is designed to eliminate cybercrime. Cyber security can also be
referred to as IT security.
Cyber security is the backbone of the network and information
security. Cyber security applies various techniques to safeguard data from data
breaches. As organizations move online, there is an increasing need for cyber
security to protect data from malicious activities.
Cyber criminality is a kind of criminal behavior involving
unauthorized access to computer systems. The number of attacks is increasing
day by day. Hackers are becoming smarter in their activities. The importance of cyber security now is more
than ever.
Cyber security gives in-depth knowledge about how to control or
recover from cyberattacks.
Conclusion
India was the country with the highest number of cybercrimes in
2020, amounting to 4.5 million. Cybercrime refers to criminal behavior
committed by using a computer or other electronic device connected to the
internet. This blog provides information about cybercrime, the various risks it
poses, and the strategies for prevention from the same.
Cybercrime is the criminal behavior of unauthorized access to
computer systems. Cyber security provides a thorough understanding of how cyber
attacks can be controlled or recovered. Online courses provide advice on how
cyber crimes and cybercrime hazards can be prevented, protected, and recovered.










Comments
Post a Comment